Experts emphasize the urgent need for investments in infrastructure and technology to ensure a sustainable water supply.
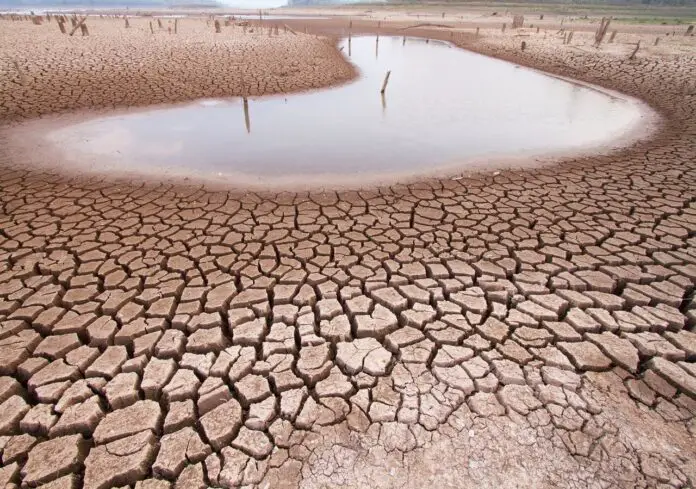
Mexico City has experienced uninterrupted drought conditions for over 16 months, affecting 100% of its territory. According to the Mexican Drought Monitor (MSM) by the National Water Commission (Conagua), this extended drought period makes it the longest-lasting issue in the city’s history as of May 15, 2024.
At the beginning of 2023, the entire city was categorized as “abnormally dry” (D0), but it quickly escalated to severe drought (D2), impacting the availability of water resources.
The Cutzamala System, which supplies approximately 30% of the city’s drinking water, faces significant challenges due to the prolonged drought. The water levels in the Cutzamala dams have significantly decreased, jeopardizing their capacity to meet the growing demand, as highlighted by Sergio Rezendez, director at Colliers Monterrey.
Cost Implications:
– Low water levels lead to increased distribution costs, from purification processes to household delivery. Sediment and contaminants become more concentrated, making water treatment more difficult and expensive.
– Infrastructure maintenance becomes crucial to prevent damage caused by sediment accumulation in pipes, resulting in additional costs and supply interruptions.
Energy-Intensive Pumping:
– The Cutzamala System spans over 127 kilometers, involving dams, canals, pumping stations, and treatment plants.
– Pumping water from the State of Mexico and Michoacán to Mexico City requires substantial energy. The water must be lifted more than 1,100 meters to reach storage tanks in the capital.
– High energy costs associated with pumping contribute to the overall operational expenses of the water supply system.
Economic Impact:
– Mexico City relies on 93% of its water for urban, public, and domestic use, affecting the entire population.
– Basic services, including hospitals and households, suffer when water quality declines or rationing occurs, leading to health risks.
– The service sector, including restaurants and commercial buildings, faces increased costs due to water scarcity.
– The ongoing water crisis may influence business decisions regarding location and investment.
While Mexico City remains a vital business hub, water-related challenges could impact its attractiveness for future investments. Companies hope for relief through rainfall, but the prolonged drought and rising costs may prompt reevaluation of their operations’ location.
Challenges in Water Distribution Infrastructure
The aging and deteriorating water distribution infrastructure faces significant challenges. Pipes and delivery systems are susceptible to leaks, resulting in substantial water loss before it reaches consumers. Authorities estimate that up to 40% of water is lost due to leaks in the distribution network—an alarming statistic that exacerbates the water crisis during drought periods.
Experts emphasize the urgent need for investment to address Mexico City’s water crisis. Prioritizing the modernization of existing infrastructure is crucial. Many pipe systems and water treatment plants are outdated and suffer from significant leaks and losses. Renewing and modernizing this infrastructure is essential to reduce losses and enhance water supply efficiency.
Source: El Economista